How does this support my pentesting career?
- SSL/TLS certificates validation relies on DNS
- Mounting spoofing attacks
- Performing information gathering
- The Domain Name System, or DNS, is the only application layer of the protocol you will see in this module.
- The DNS primarily converts human-readable names, like elearnsecurity.com, to IP addresses and is a fundamental support protocol for the Internet and computer networks in general. It is widely recognized that the entire internet security is relying upon DNS.
- You will need to know how the DNS service provides name resolution because every common operation on the Internet such as opening a website, sending an email, and sharing a document involves the use of a DNS to resolve resource names to IP addresses (and vice versa).
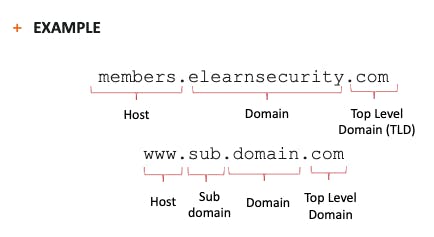
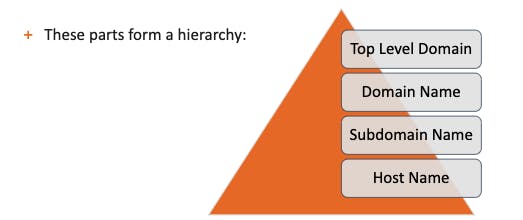
A DNS name such as elearnsecurity.com or members.elearnsecurity.com can be broken down into the following parts:
- Top-level domain (TLD)
- Domain part
- Subdomain part (if applicable)
- Host part
DNS Structure :
- Name resolution is performed by resolvers, servers that contact the top-level domain (TLD) DNS servers and follow the hierarchy of the DNS name to resolve the name of a host.
- Resolvers are DNS servers provided by your ISP or publicly available like OpenDNS or Google DNS.
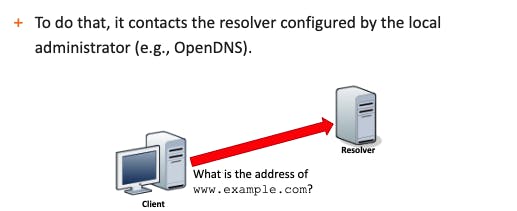
- To convert a DNS name into an IP address, the operating system must contact a resolver server to perform the DNS resolution.
- The resolver breaks down the DNS name in its parts and uses them to convert a DNS name into an IP address.
DNS Resolution Algorithm :
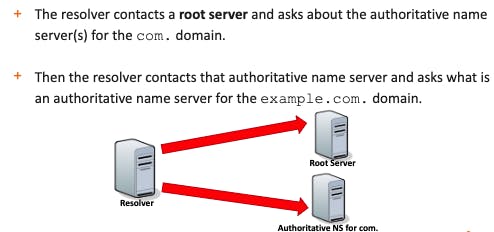
1- Firstly, the resolver contacts one of the root name servers; these servers contain information about the top-level domains.
2- Then, it asks the TLD name server what's the name server can give information (authoritative name server) about the domain the resolver is looking for.
3- If there are one or more subdomains, step 2 is performed again on the authoritative DNS server for every subdomain.
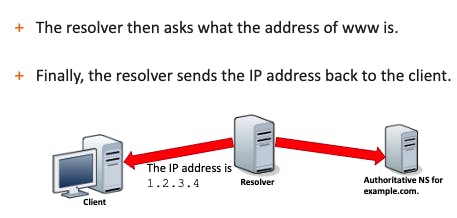
4- Finally, the resolver asks for the name resolution of the host part.
EX :

Then
After That
Finally
--> How can a resolver know how to contact a root name server?
--> IP addresses of the root servers are hardcoded in the configuration of the resolver. System administrators keep the list updated, otherwise, the resolver would not be able to contact a root server!
The domain name system can also perform the inverse operation; it can convert an IP address to a DNS name.
Keep in mind that this is not always the case; the administrator of a domain must have enabled and configured this feature for the domain to make it work.
Written by : Mohamed Abdalla Ibrahim
PMP | CISM | ITIL | CEH | Azure Architect | Azure Security Engineer | IBM Cybersecurity Analyst

